Road marking paint is crucial for traffic safety, lane organization, and parking management. Among various types, thermoplastic (hot-melt) and cold spray (cold-plastic) road marking paints are the two most commonly used technologies. What are their differences, and how should you choose? Below is a comparative summary based on relevant information:
1. Composition and Form
Thermoplastic Road Marking Paint
- Form: Solid powder or granules at room temperature.
- Main Components: Synthetic resins (e.g., C5 or C9 hydrocarbon resins), glass beads (for reflectivity), pigments, fillers (e.g., calcium carbonate), and additives.
- Preparation: Must be heated and melted into a liquid state in a thermoplastic furnace or preheater before use.
Cold-Spray Road Marking Paint
- Form: Ready-to-use liquid (solvent-based, water-based, or two-component acrylic/epoxy formulations).
- Primary Components: Binder (alkyd resin, acrylic resin, or epoxy resin), solvent or water, pigments, fillers, and additives. Reflective glass beads may be added during or after spraying.
- Preparation: Typically requires stirring; in some cases, dilution with thinner is needed to adjust viscosity.
2. Application Process and Equipment
Thermoplastic Markings
- Temperature: Must be heated to 180°C–210°C (356°F–410°F) in a dedicated road marking machine equipped with a melting furnace.
- Application Equipment: Requires a thermoplastic road marking machine, typically including a preheater, pressurized sprayer, and glass bead applicator.
- Process: Extruded or sprayed onto the pavement, the molten material rapidly solidifies upon contact. This process involves open flame or electric heating, necessitating trained operators and strict safety protocols.
- Line Width: Typically 1.5 mm to 2.5 mm, forming durable raised markings.
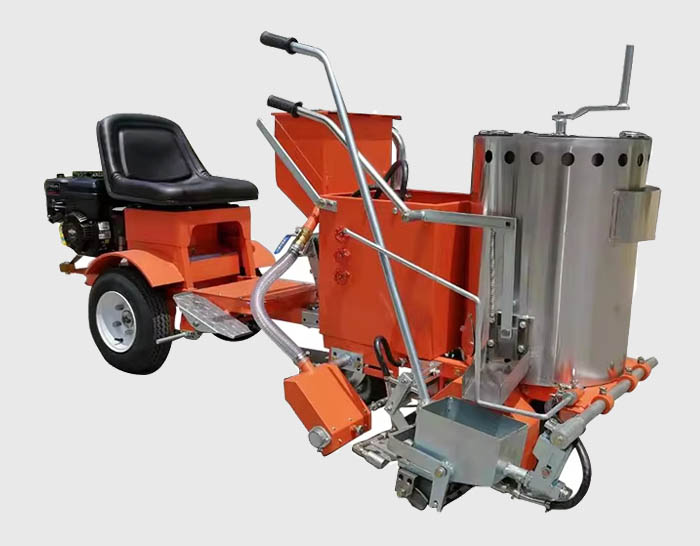

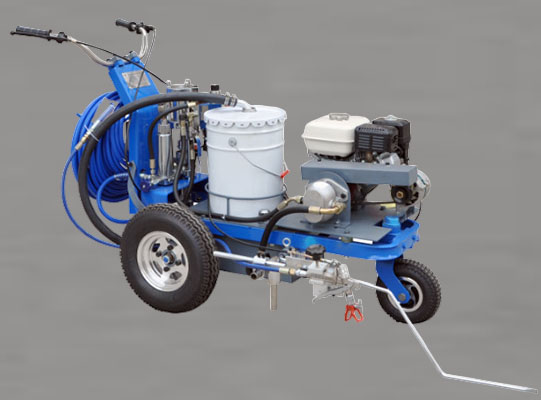
Cold Spray Markings
- Temperature: Applied at ambient temperatures without heating.
- Application Equipment: Can be applied using airless sprayers, roller applicators, brush techniques, or simple line markers. Vehicle-mounted road marking machines are typically used for large projects.
- Process: Liquid coating is sprayed or rolled onto the surface, drying through solvent evaporation or chemical curing (two-component systems).
- Coating thickness: Typically 0.3 mm to 0.9 mm, forming a thin, smooth paint film.

3. Performance and Durability
Thermoplastic Paint
- Durability: Highly abrasion-resistant, withstands heavy vehicle traffic, and exhibits strong weather resistance. Typical lifespan on high-traffic roads is 2 to 5 years.
- Visibility: Excellent retroreflectivity due to embedded glass beads, enhancing nighttime visibility and road safety.
- Weather Resistance: Performs well under extreme temperatures, UV exposure, and chemicals (e.g., deicing salts).
Cold Spray Paint
- Durability: Lower abrasion resistance due to thinner film thickness. Service life ranges from 3 to 12 months depending on formulation and traffic volume.
- Visibility: Reflectivity depends on surface-applied glass beads, which may wear off more quickly.
- Best Use: Low-traffic areas, temporary markings, indoor parking lots, and projects requiring fast, low-cost application.
4. Safety and Environmental Impact
Thermoplastic Paint
- Safety Risks: High-temperature operations pose burn and fire hazards. Proper ventilation must be provided to control fume emissions.
- Environmental Considerations: While typically VOC-free after curing, the heating process may release trace amounts of volatile organic compounds.

Cold Spray Paint
- Safety: Safer application without heating.
- Eco-Friendly Option: Water-based cold spray paint is low in VOCs, odorless, and non-flammable, making it suitable for enclosed spaces and environmentally sensitive areas.
- Precautions: Solvent-based cold spray paint contains VOCs, requiring proper respiratory protection and ventilation.
5. Cost Analysis
Hot-Melt Paint
- Initial Cost: Higher due to specialized road marking equipment and energy consumption.
- Material Consumption: Approximately 4–5 kg/m².
- Long-Term Value: Longer lifespan and lower recoating frequency result in lower lifecycle costs for permanent installations.
Cold Spray
- Initial Cost: Lower; required application tools are also more economical.
- Material Consumption: Approximately 0.2–0.3 kg/m² for film spraying.
- Long-Term Considerations: More frequent recoating may increase long-term labor and material costs.
6. Surface Preparation and Maintenance
Thermoplastic Paint
- Surface Requirements: Pavement must be clean, dry, and ideally warm for optimal adhesion.
- Rerouting: Existing thermoplastic markings typically require mechanical removal (grinding, sandblasting) before recoating to ensure adhesion and achieve a smooth surface.
Cold Spray Paint
- Surface Requirements: Clean, dry surface; some formulations tolerate slight moisture.
- Rerouting: Can usually be applied directly over old markings (after cleaning), simplifying maintenance and renewal.
7. Recommended Applications
| Scenario | Recommended Paint Type | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Highways & Expressways | Hot Melt (Thermoplastic) | Superior durability, reflectivity, and weather resistance for high-speed traffic. |
| Urban Roads & Intersections | Hot Melt or Two-Component Cold | Balance of longevity and performance under moderate to heavy traffic. |
| Parking Lots & Private Roads | Cold Spray (Water-Based or Solvent) | Cost-effective, easy application, suitable for periodic remarking. |
| Temporary Markings & Construction Zones | Cold Spray | Quick setup, easy removal or overlay. |
| Airports & Seaports | Two-Component Cold or Hot Melt | Extreme durability required for heavy machinery and fuel resistance. |
| Bike Lanes & Pedestrian Paths | Cold Spray (Water-Based) | Eco-friendly, low-odor, safe for public spaces. |
Selecting the Right Road Marking Paint
Choosing between thermoplastic or cold spray road marking materials depends on several key factors:
- Traffic Volume and Road Type: High-traffic roads require durable materials like thermoplastics.
- Budget Constraints: Consider both initial and long-term costs.
- Environmental Regulations: Prioritize eco-friendly, low-VOC road marking paints.
- Project Timeline: Cold-applied markings offer faster installation with minimal equipment requirements.
- Climate Conditions: Hot-applied markings perform better in extreme weather; cold-applied markings may suit temperate climates.
- Marking Lifespan: Evaluate maintenance cycles and expected service life.
Both hot melt road marking paint and cold spray road marking paints play vital roles in modern traffic management and pavement delineation. Thermoplastic paint offers unmatched durability for high-traffic highways and permanent markings, while cold spray paint provides flexibility, lower upfront costs, and ease of application for temporary or low-traffic applications. Investing in the right road line marking machine and material not only improves visibility and guidance for drivers but also contributes to efficient and sustainable infrastructure management. For more information on road marking standards, application techniques, or product specifications, contact us for complimentary professional solutions.
